Big Data Analytics of Northeast Asia’s Top 10 News Topics
Text analytics are widely used to extract information and patterns from text. By applying a combination of such text analytics techniques to newspaper articles, priorities and patterns in the news can be identified. In an attempt to establish the Asia-related issues that concerned the countries of Northeast Asia the most in recent years, newspaper articles were analyzed by researchers based at Seoul National University Asia Center, working in association with staff from of Ars Praxia, a company specializing in big data analytics and digital contents creation. The analyzed data consisted of Asia-related news articles published in the English-language newspapers of South Korea, China, Japan, and the United States between January 1, 2020 and September 30, 2022.
The original data set comprised a total of 5,502,266 articles from 824 news outlets. In order to mitigate the bias arising from the fact that 4,796,149 of these articles came from American news outlets, additional sampling was undertaken. The data set that was analyzed consisted of the following number of articles: 46,036 (South Korea); 76,171 (China); 44,298 (Japan); 94,521 (USA). Topic analysis was undertaken on these articles using topic modeling, trend analysis, and semantic analysis techniques.
Using topic modeling, which is a machine learning technique that that analyzes unstructured text data in order to recognize latent topics, the top ten Asia-related news topics were identified and then their relative importance was established for each country. All four countries showed a high interest in economic crisis and energy related crisis. In addition, the North Korean nuclear crisis was commonly regarded as a topic of relative high interest in South Korea and Japan. On the other hand, cross-strait issues and security crises (which included issues such as tension in the Taiwan Strait and fishery disputes) were only a high-interest topic for Chinese news outlets.
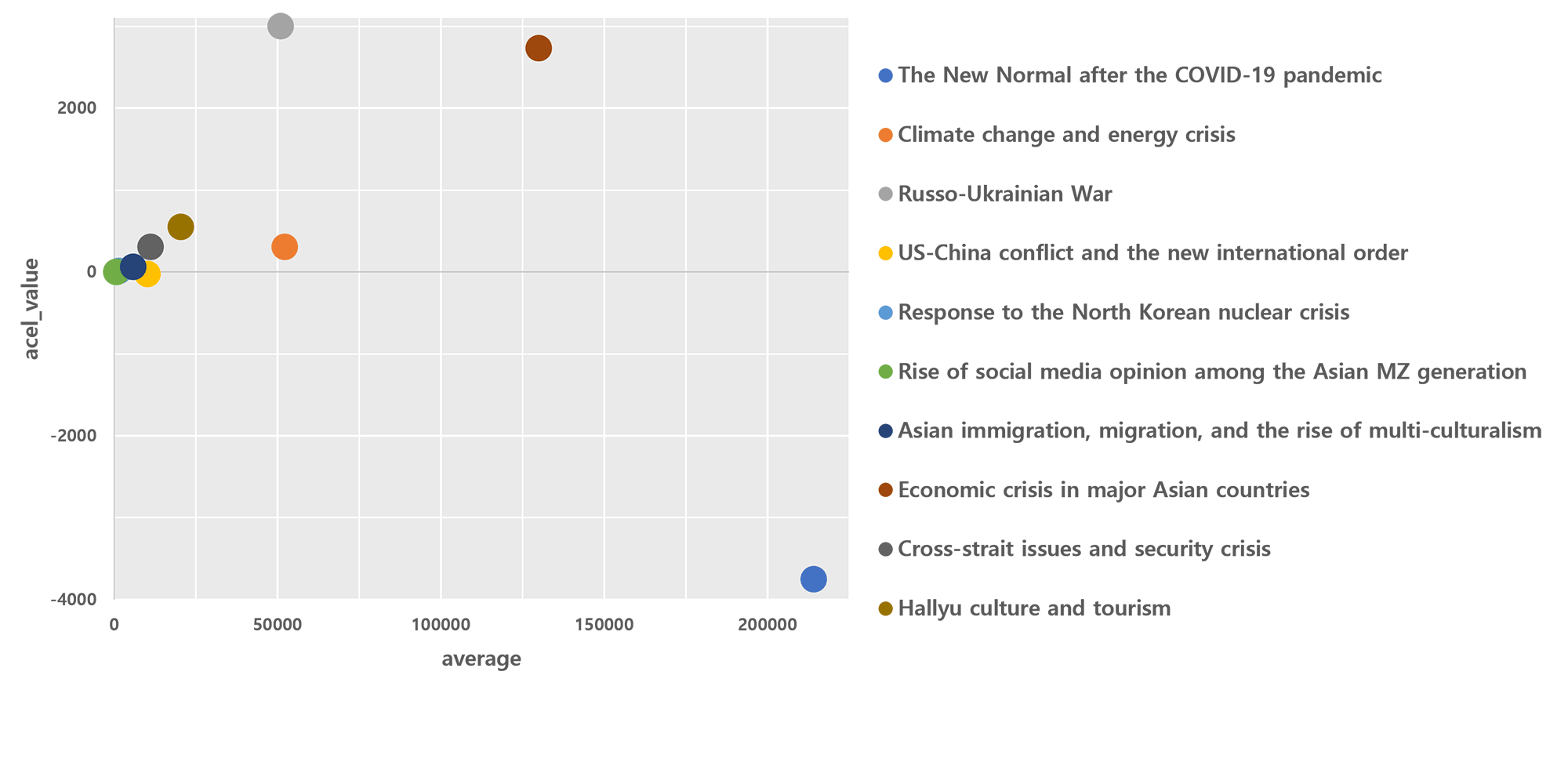
Fig. 1: Article frequency (X-axis) and acceleration (Y-axis) for the top ten topics (January 1, 2020 to Sept. 30, 2022). (Figure by the authors, 2023)
Then how did interest in these ten topics change over time? In order to explore this question, trend analysis was carried out. The article frequency of each topic was calculated per quarter and changes in the frequency were traced over time. As illustrated in Figure 1, the number of articles on the COVID-19 pandemic was overwhelmingly high, with an average of 214,000 articles per quarter. However, in terms of relative acceleration, this topic had the lowest negative value (-3751.17), suggesting that interest in this topic will soon disappear. The economic crises of major Asian countries, on the other hand, is a topic characterized by both high frequency (130030.55) and acceleration (2735.57) in terms of average articles per quarter. This indicates that the countries of Northeast Asia and the United States expect this issue to become a constant threat in the near future. The Russo-Ukrainian war, believed to play a pivotal role in determining the direction of the international order in 2023, illustrated the third highest average frequency (50954.27) and the highest acceleration (3001.56).
Semantic network analysis was used to identify the keywords of interest, as well as the relationships between these keywords, for each the four countries. The semantic network of the articles from the news outlets of all four countries reveals that ‘engine’ (of economic growth), ‘COVID strategy,’ ‘energy supply,’ ‘technology,’ ‘cruise missile,’ and ‘stock price’ were the most frequently occurring keywords [Fig. 2].
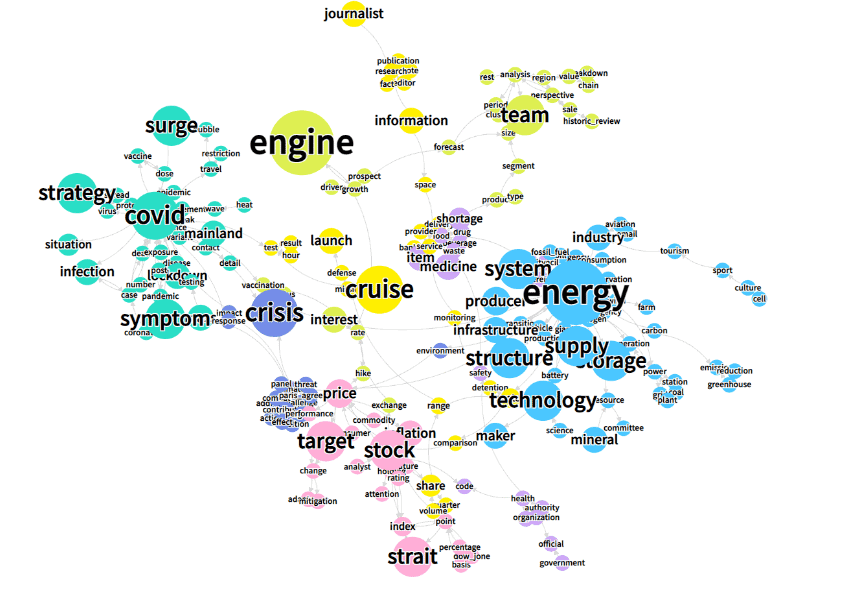
Fig. 2: Semantic network of Asia-related news articles from the English news outlets of South Korea, China, Japan and the USA (January 1, 2020 to Sept. 30, 2022). (Figure by the authors, 2023)
Using the nodes (keywords) with the highest betweenness centrality values, the shared or unique key interests of each of the four countries were then identified and visualized, as presented in Figure 3. It can be observed that ‘energy,’ located in the center, was the key interest shared by all four countries. Common key interests are expressed as nodes placed between the respective countries, and unique interests are expressed as dots located along the periphery of each country node. Inflation (represented by ‘price’) was a common concern to the three Northeast Asian countries, and South Korea and Japan also shared concerns about the missiles launched by North Korea. It is of interest to note that, for China, ‘health’ was identified to be a key interest, alongside ‘development,’ ‘security,’ and ‘trade.’ This suggests that the government’s handling of the pandemic at home has come to be regarded as a key issue affecting government stability.
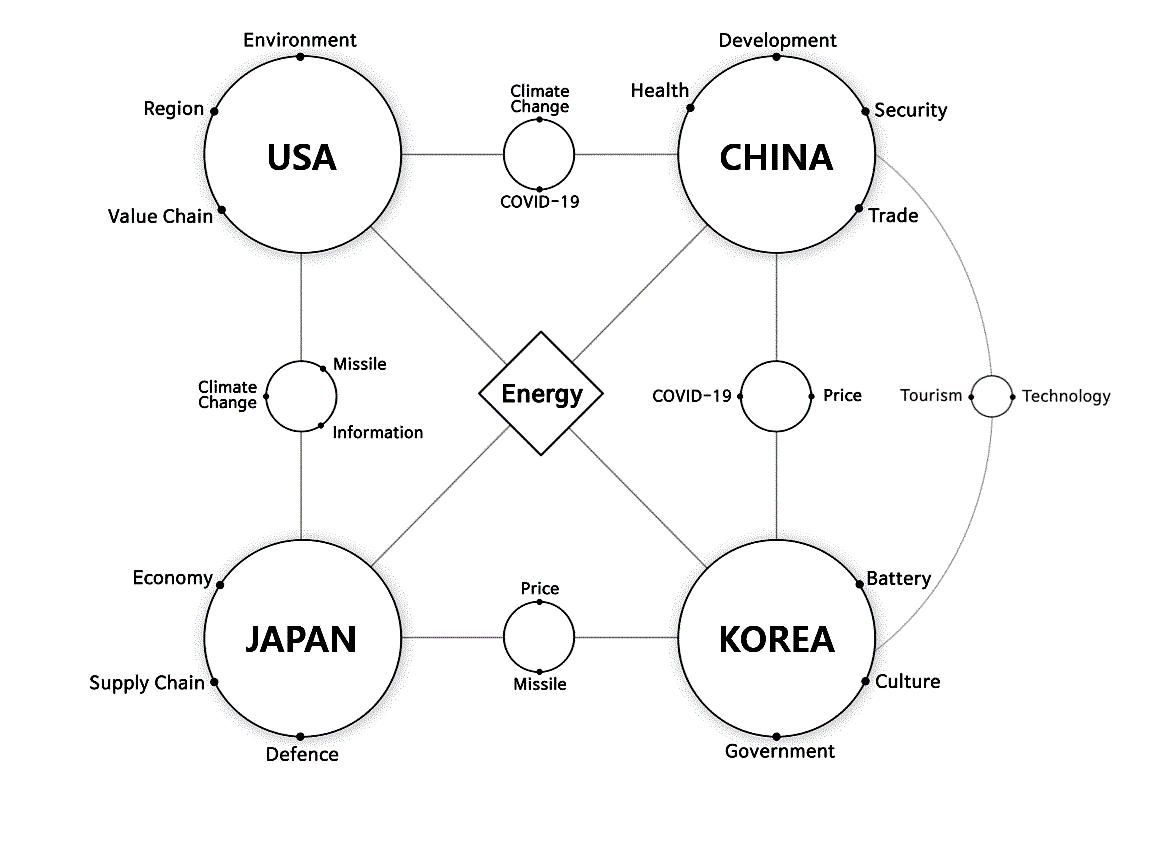
Fig. 3: Shared or unique key interests as seen through Asia-related news articles from the English news outlets of South Korea, China, Japan and the USA (January 1, 2020 to Sept. 30, 2022). (Figure by the authors, 2023)
These results of Big Data analytics clearly show the complex security risks that have emerged due to the geopolitical shifts of the post-COVID-19 era. With the possibility of escalating military conflicts, such as those between Russia and Ukraine, the concept of ‘security’ has expanded and evolved to include responses to climate and environmental crises, public health crises, the securing of value chains, protection of technological competitiveness, and well-controlled trade and economy. It will be interesting to trace the predictive nature of these results of big data analytics in order judge the viability of Big Data analytics as an alternative research tool for gaining insights into the region.
Myungmoo Lee, Seoul National University Asia Center. Email: leemm@snu.ac.kr
Dohoon Kim, Ars Praxia. Email: leo_kim@arspraxia.com